
A Sandor Initiative Towards Richer Clinical Insights
CASE BULLETINS
Disclaimer: This newsletter is intended to enrich the insights related to genetic disorders from a laboratory perspective. The objective of this newsletter is to share knowledge from a lab perspective to facilitate the dialogue of genetic disorders diagnosis. We want to sincerely thank the physicians whose dedication, knowledge and intelligence helps arrive at answers through diagnosis enabling timely and effective prevention.

ABOUT THE DISEASE
Krabbe disease (also called globoid cell leukodystrophy) is a severe neurological condition. It is part of a group of disorders known as leukodystrophies, which results from demyelination in the nervous system. Krabbe’s is a monogenic disorder caused by the mutation in the GALC gene and has an autosomal recessive inheritance¹ . The early-onset type of Krabbe disease is the most common and the most severe.Babies who have early-onset (infantile) Krabbe disease typically develop features in the first six months of life.Symptoms of infantile Krabbe disease may include irritability, failure to thrive, slowed development, and unexplained fevers.
These are followed by progressive muscle weakness, hearing and vision loss, and decreased movement. Symptoms of the later-onset types of Krabbe disease start in childhood, early adolescence, or adulthood. These may include muscle weakness & stiffness, loss of milestones, blindness, behavior problems, dementia, and seizures ².
CASE REFERRED TO SANDOR
A Female Baby Born Of Second-degree Consanguineous Marriage Of Age 5 Months Presented With:
- Regression of milestones (cognitive & motor)
- Visual impairment
- Muscle weakness
- Bulbar dysfunction
- Myoclonic jerks
- Brain MRI observed with periventricular hyperintensities, thalamic hypodensity, pyramidal trait
Tests Prescribed
- Enzyme Analysis for Beta Galactocerebrosidase
- Clinical Exome Sequencing
| Test Name | Sample Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme Analysis for Beta Galactocerebrosidase |
2-4 ml Sodium Heparin Blood | Fluorometry assay with artificial substrate | Assay carried on leukocytes |
| Clinical Exome Sequencing | 2-4 ml EDTA Blood | Next Generation Sequencing | Mean coverage of 80-100X coverage. Target coverage 200X |
- Enzyme Analysis: Baby was found to have low Beta Galactocerebrosidase activity (0.08 nmol/17hr/mg) vs. biological reference range 4-40 nmol/17hr/mg).
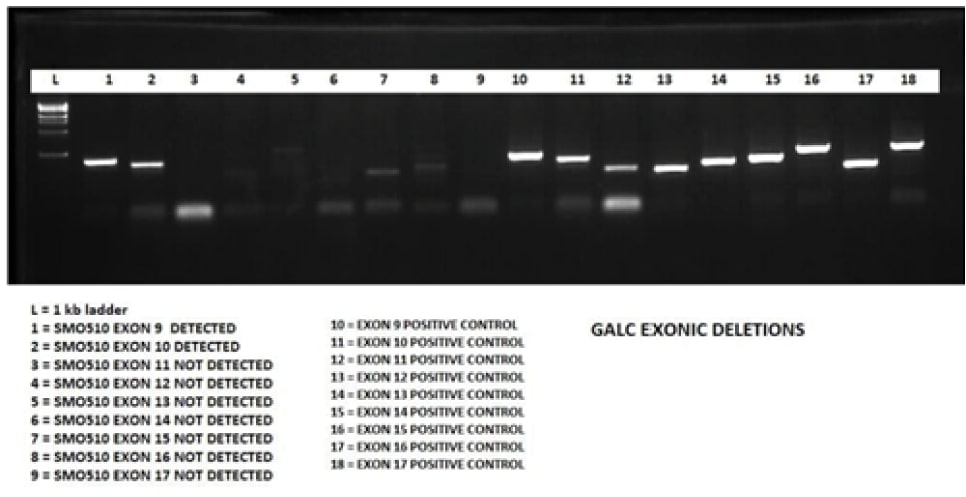
- Clinical Exome Sequencing: In Exome data, homozygous deletion was suspected from Exon 11-17 in GALC gene. However, in order to confirm the results, an in-house PCR testing was performed, that confirmed the homozygous deletion.
- The recommended first-tier test for Krabbe disease is GALCW / Galactocerebrosidase, Leukocytes.
- Individuals with GALC activity below the reference range for these assays are more likely to have variants in the GALC gene that are identifiable by molecular genetic testing³.
- Variants of uncertain significance (VUS) also cause decreased GALC activity, hence these variants can be potentially disease causing if there is a decrease in GALC activity
- Exome sequencing along with enzyme activity analysis can significantly improve the diagnostic yield.
| Name | Designation | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Ms. Krishnendu Menon | Manager-Scientific Affairs | Compilation |
| Ms. Vineeta Singh | Vice President-Scientific Affairs | Exome Analysis |
| Ms. Divya Borkar | Manager - Biochemical Genetics | Enzyme Assay |
References:
- 1Medline Plus,https://medlineplus.g...Click here
- ²Rare Diseases,NIH,https://rarediseases....Click here
- ³Mayo Clinichttps://www.mayocliniclabs...Click here